Bitcoin Price and Value
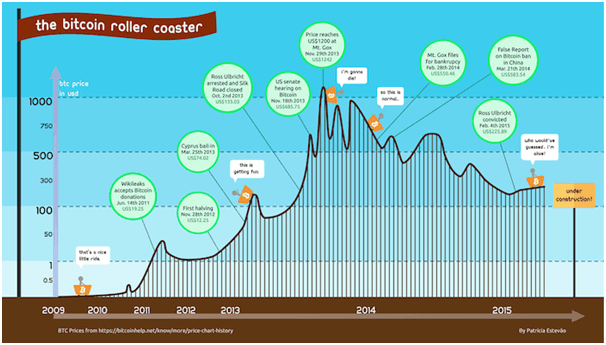
“Bitcoin’s Price Breaks Out of Range to Reach $900”- Well this might sound good to many investors as the price of bitcoin surged in January 2017 rising more than 9% and exceeding $900 for the first time in nearly a week the highest as observed by USD Bitcoin price index.
But a newbie to Bitcoin must be wondering how Bitcoin are priced and values across the market are determined. Here below you can find such answers of how this cryptocurrency has value.
Creating Bitcoins
First to understand things better you should know how bitcoins are generated. New bitcoins are generated by a competitive and decentralized process called “mining”. This process involves that individuals are rewarded by the network for their services. Bitcoin miners are processing transactions and securing the network using specialized hardware and are collecting new bitcoins in exchange.
The Bitcoin protocol is designed in such a way that new bitcoins are created at a fixed rate. This makes Bitcoin mining a very competitive business. When more miners join the network, it becomes increasingly difficult to make a profit and miners must seek efficiency to cut their operating costs. No central authority or developer has any power to control or manipulate the system to increase their profits. Every Bitcoin node in the world will reject anything that does not comply with the rules it expects the system to follow.
Bitcoins are created at a decreasing and predictable rate. The number of new bitcoins created each year is automatically halved over time until bitcoin issuance halts completely with a total of 21 million bitcoins in existence. At this point, Bitcoin miners will probably be supported exclusively by numerous small transaction fees.
Bitcoins have value
Bitcoins have value because they are useful as a form of money. Bitcoin has the characteristics of money (durability, portability, fungibility, scarcity, divisibility, and recognizability) based on the properties of mathematics rather than relying on physical properties (like gold and silver) or trust in central authorities (like fiat currencies). In short, Bitcoin is backed by mathematics. With these attributes, all that is required for a form of money to hold value is trust and adoption. In the case of Bitcoin, this can be measured by its growing base of users, merchants, and startups. As with all currency, bitcoin’s value comes only and directly from people willing to accept them as payment.
What determines bitcoin’s price? 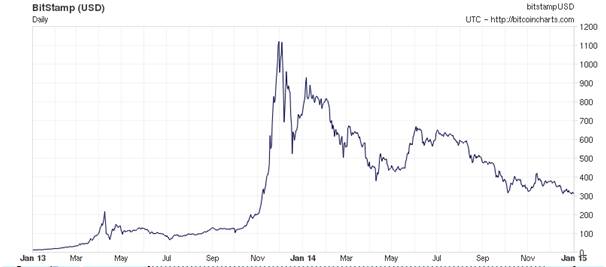
The price of a bitcoin is determined by supply and demand. When demand for bitcoins increases, the price increases, and when demand falls, the price falls. There is only a limited number of bitcoins in circulation and new bitcoins are created at a predictable and decreasing rate, which means that demand must follow this level of inflation to keep the price stable. Because Bitcoin is still a relatively small market compared to what it could be, it doesn’t take significant amounts of money to move the market price up or down, and thus the price of a bitcoin is still very volatile.
The Bitcoin price has been highly unpredictable but has proven to be one of the best speculations ever with multiple years having returns in excess of 5,000% each.
Bitcoin price over the time can even become worthless
In history you see how currencies that failed and are no longer used, such as the German Mark during the Weimar Republic and, more recently, the Zimbabwean dollar. Although previous currency failures were typically due to hyperinflation of a kind that Bitcoin makes impossible, there is always potential for technical failures, competing currencies, political issues and so on. As a basic rule of thumb, no currency should be considered absolutely safe from failures or hard times. Bitcoin has proven reliable for years since its inception and there is a lot of potential for Bitcoin to continue to grow. However, no one is in a position to predict what the future will be for Bitcoin.
Important factors to consider Bitcoin to be valuable
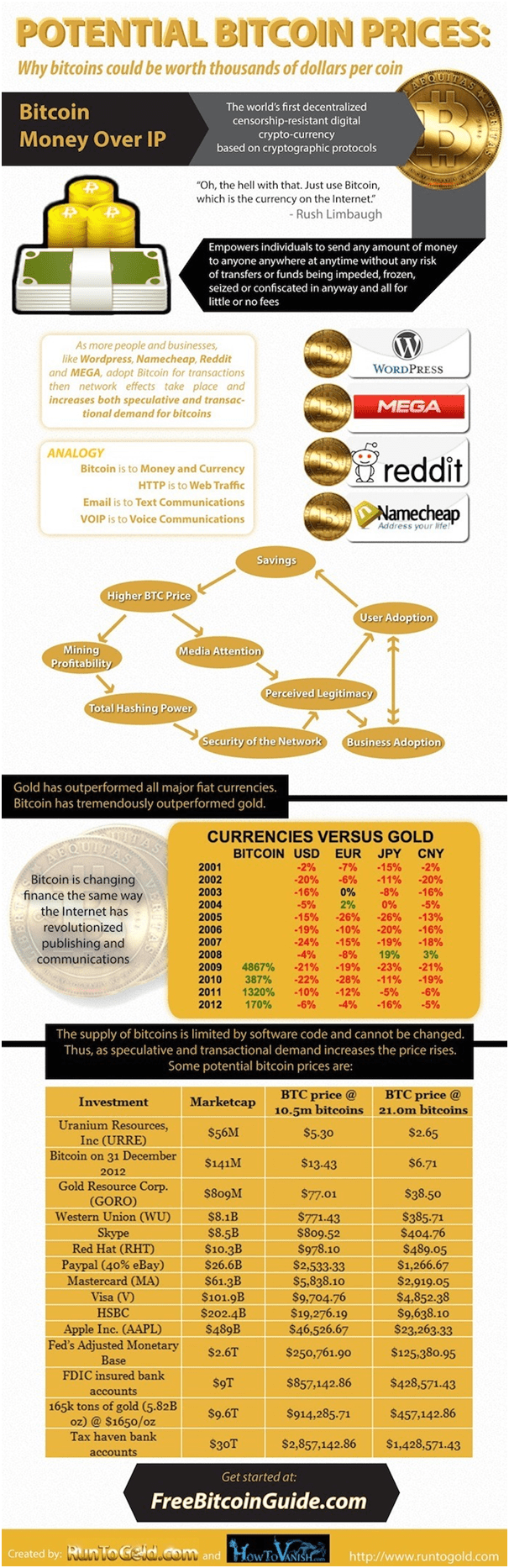
Bitcoin’s value is a perceived regard for its benefits and usefulness. Value is not the price as they both are different. Price is the monetary cost of a bitcoin. The usefulness and consequent value of Bitcoin is a result of many aspects of its innovation, its network, and its features. (source:cryptocoins)
Scientific Value
To the general field of Science, the Bitcoin innovation is valuable for having solved the long-standing Two Generals Problem (or Byzantine Generals’ Problem). The solution to the dilemma of digital double-spending is achieved via a self-organizing and time-based consensus record. The blockchain, a shared public ledger, is maintained by the peer-to-peer nodes that populate the Bitcoin network.
Technological Value
As Bitcoin is decentralized via a distributed peer-to-peer network, there is no central server that the Bitcoin protocol depends upon for its existence. Like BitTorrent, Bitcoin is, therefore, censorship-resistant – it cannot be shut down. This aspect of Bitcoin is critical since it means that Bitcoin’s continued usage is not subject to any external authority’s approval, opinion or action. Being a censorship-resistant alternative to official currency and payment systems makes Bitcoin an irreversible disruptive technology.
When Satoshi released the software in January 2009 there was no Bitcoin price because there was no Bitcoin value since it could not be used for anything.
Social Value
A social implication of the way Bitcoin innovates payment and transactions is that it eliminates Trust. A distributed ledger and decentralized network means that no single entity needs to be trusted in order for the Bitcoin protocol to function. Each Bitcoin user owns and controls their own money outright, and is solely responsible for its security and usage. No third party, such as a bank or centralized issuer, needs to be implicitly trusted to hold, disburse or maintain one’s bitcoin holdings. This trust-less dimension of Bitcoin eliminates the risks associated with having to trust external authorities .
Token of Value
Although a bitcoin can be copied many times, it can only ever be spent once. This design feature can be verified by making a copy of an existing Bitcoin wallet to another computer. The same bitcoins will exist in two physical locations, but only the first spend transaction will succeed. The network will recognize a second attempt to spend the same bitcoins as a double-spend and reject it. This is the critical innovation that sets Bitcoin apart from all previous attempts at creating digital currency.
Design Value
With the solution to double-spending as its foundation, Bitcoin’s explicit design features offer users additional value like currency or payment method, secure storage and transmission, blockchain and contract mechanism.
Secured Value
Bitcoin uses public-private key pairs to secure transactions. A Bitcoin address is a public key generated from a private key held in a user’s wallet. A Bitcoin transaction destined for an address generated by a wallet is signed with that address’s public key, and can only be “unlocked” (or spent) with the matching private key. Hence, Bitcoin transactions are secured against theft. The underlying mechanism that prevents double-spending secures Bitcoin against forgery.
Development Value
Bitcoin is made available as Free and Open Source Software under the MIT license. Additionally, the protocol is also developed via the Open Source project model which encourages community contribution and collaboration.
Collaborative development of publicly available source code is considered to be preferable to closed source code developed by a contained team. Bugs and security fixes are identified and fixed quickly – and around the clock – while the principle of strength in numbers and diversity of skills allows greater productivity.
The Bitcoin Core Developers are mostly unpaid volunteers who maintain and manage the Bitcoin source code. If their work was any less critical and exciting, one could describe it as a “thankless task”, yet they represent some of the hardest working developers in the field. The core developers contribute thousands of hours of code writing and rigorous adherence to design specifications in order to translate the Bitcoin vision into reality.
Network Value
The Bitcoin network is a decentralized peer-to-peer network that, ideally, is both distributed and diverse. The more widely the peer-to-peer nodes are distributed, the more decentralized the network. The more diverse (non-similar) the nodes are, the broader the representation on the network and, hence, it is more resilient and secure. The Bitcoin protocol is designed to seek consensus amongst nodes, and greater decentralization means a healthier, more robust network. All of these factors contribute to a more valuable blockchain.
https://youtu.be/Cs6F91dFYCs
Miners Are Valuable
As said above Bitcoin Miners are rewarded bitcoins for processing transactions into blocks. Mined blocks are typically appended to the blockchain, and become part of the public ledger. By processing transactions, building the blockchain, and hosting the peer-to-peer nodes that maintain network consensus, miners represent the backbone of Bitcoin’s distributed network. For their task of keeping the network functional at all times and maintaining the precious blockchain, miners (in a close tie with the developers) are the Bitcoin protocol users who add the most value.
Value Transmission and Storage
The world’s reserve currency, along with most other national currencies, can be exchanged for bitcoins and stored or transmitted via the Bitcoin network. It seems to that, as the amount of money increases, so the benefits of using Bitcoin storage/transmission also increase.
Bitcoins in storage can be secured by different means, including passwords, biometric readers and multiple signature transactions. Although theft of, say, a password or human error can still result in loss of stored bitcoins, the risks are far less than in the case of physical assets such as paper money or gold bullion. Transmitting bitcoins via the payment network is cheaper and faster than transferring an equivalent amount via traditional channels, and less cumbersome and more secure than transporting an equivalent amount of bullion.
Contract and Application Value
Bitcoin Contracts are described by Satoshi Nakamoto, although this aspect of the protocol has found few applications to date. Contracts extend the multi-signature facility of Bitcoin by allowing two or more parties to engage in agreements that are fulfilled by events that are external to the Bitcoin network. Examples include Options Contracts, Wills and even simple binary bets such as the outcome of the Brazilian Women’s Volleyball match. In the future, this facility of Bitcoin will be better understood, used more frequently and add more value to the protocol.
The distributed blockchain is designed to accommodate alternate chains, thereby opening the door to applications that both use and enhance the Bitcoin protocol. These distributed applications will add value by making Bitcoin more useful.
So you see that Bitcoin’s value cannot be reduced to one single element or feature. Many aspects of the cryptocurrency contribute to its usefulness and offer benefits that outweigh traditional paper money and its encumbent systems.